

#Concussion after effects professional#
In these cases, you should be checked by a health professional trained in assessing head injuries. been drinking alcohol or taking recreational drugs.had an operation on your brain in the past or are taking blood-thinners (like warfarin).changes in your behaviour, such as becoming more irritable.been vomiting since the injury - more than one episode in an adult or three or more episodes in a child.Go to your nearest emergency department if you've injured your head and have: You probably don't have concussion, and can follow the advice about treating a minor head injury at home.Ĭall your GP or GP out of hours service for advice if you're not sure if you need medical help. a headache that goes away on its own or is relieved by painkillers.You don't usually need to get immediate medical advice if you only have mild symptoms that don't last long after a head injury, such as: What to do if you think you might have concussion Treat a minor head injury at home

The main things to look for would be a change in normal behaviour after a head injury, such as crying a lot, a change in their feeding or sleeping habits, or a loss of interest in people or objects. Many of the signs above would be difficult to spot.
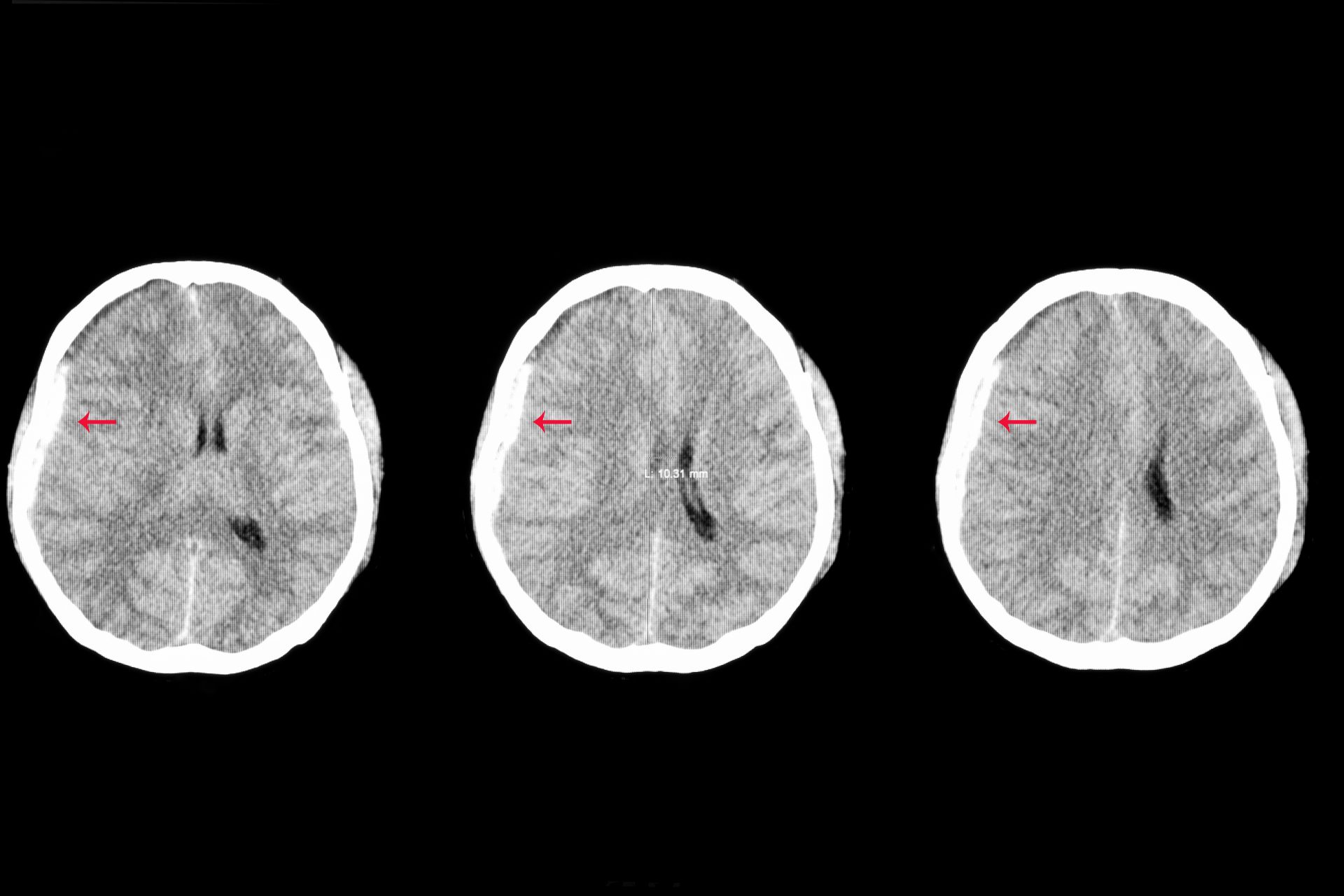
The brain degeneration is associated with common symptoms of CTE including memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment, impulse control problems, aggression, depression, suicidality, parkinsonism, and eventually progressive dementia. These changes in the brain can begin months, years, or even decades after the last brain trauma or end of active athletic involvement. The pattern of tau seen in the brains of those with CTE is distinct from other neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), progressive supra nuclear palsy (PSP), and corticobasal degeneration (CBD). The repeated brain trauma triggers progressive degeneration of the brain tissue, including the build-up of an abnormal protein called tau in a unique pattern. In recent years, reports have been published of neuropathologically confirmed CTE found in other athletes, including football and hockey players (playing and retired), as well as in military veterans who have a history of repetitive brain trauma. CTE is not limited to current professional athletes it has also been found in athletes who did not play sports after high school or college. CTE has been known to affect boxers since the 1920’s (when it was initially termed punch drunk syndrome or dementia pugilistica). Subconcussive hits are routine in many sports, including checking in ice hockey and heading the ball in soccer. These may include symptomatic concussions as well as subconcussive hits that do not cause symptoms. Frequently Asked Questions about CTE What is CTE?Ĭhronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive degenerative disease of the brain found in people with a history of repetitive head impacts (RHI) often incurred during contact sport play, military service, and other activities that involve repeated blows to the head.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
